After a blistering year, the housing market shows no sign of retreat entering 2022.
Demand continues apace, especially in cities in the Mountain West and Southeast where population growth has been particularly strong, while the number of homes available for purchase has not kept up. Consequently, price growth has been meteoric during the pandemic, and while that may slow, it’s not happening yet.
The median price for existing homes grew by 13.9% year over year in November, according to the National Association of Realtors. The Case-Shiller home price index, which accounts for same-property transactions but is slightly lagged, grew by 19.1% from October 2020 to October 2021.
Home price trends are hard to reverse. Recent sales comparables drive valuations for buyers and sellers, and with prices growing at a rapid clip, it’s unlikely that that momentum will slow. Just over 42% of home sales closed above the asking price in the four-week period ending on Dec. 26, 2021, compared to about 20% in the same period in 2019, according to real estate brokerage Redfin.
Given this recent history, it may not be surprising that projections for home prices in 2022 are all over the place, ranging from continued strong price increases to declines. But a variety of factors influence the direction of the housing market, making the effort to produce forecasts challenging.
Millennial Demand Drives Prices Higher
A significant driver of housing demand will continue to come from millennials, who are aging into their first-time home-buying years. They have made up a large portion of homebuyers for the past few years, but a large share is yet to reach their 30s when owning a home becomes a larger priority. And although many millennials preferred urban areas prior to the pandemic, hybrid work schedules and flexible work-from-home policies have attracted many to move to suburban areas where home prices tend to be more affordable and construction is more feasible.
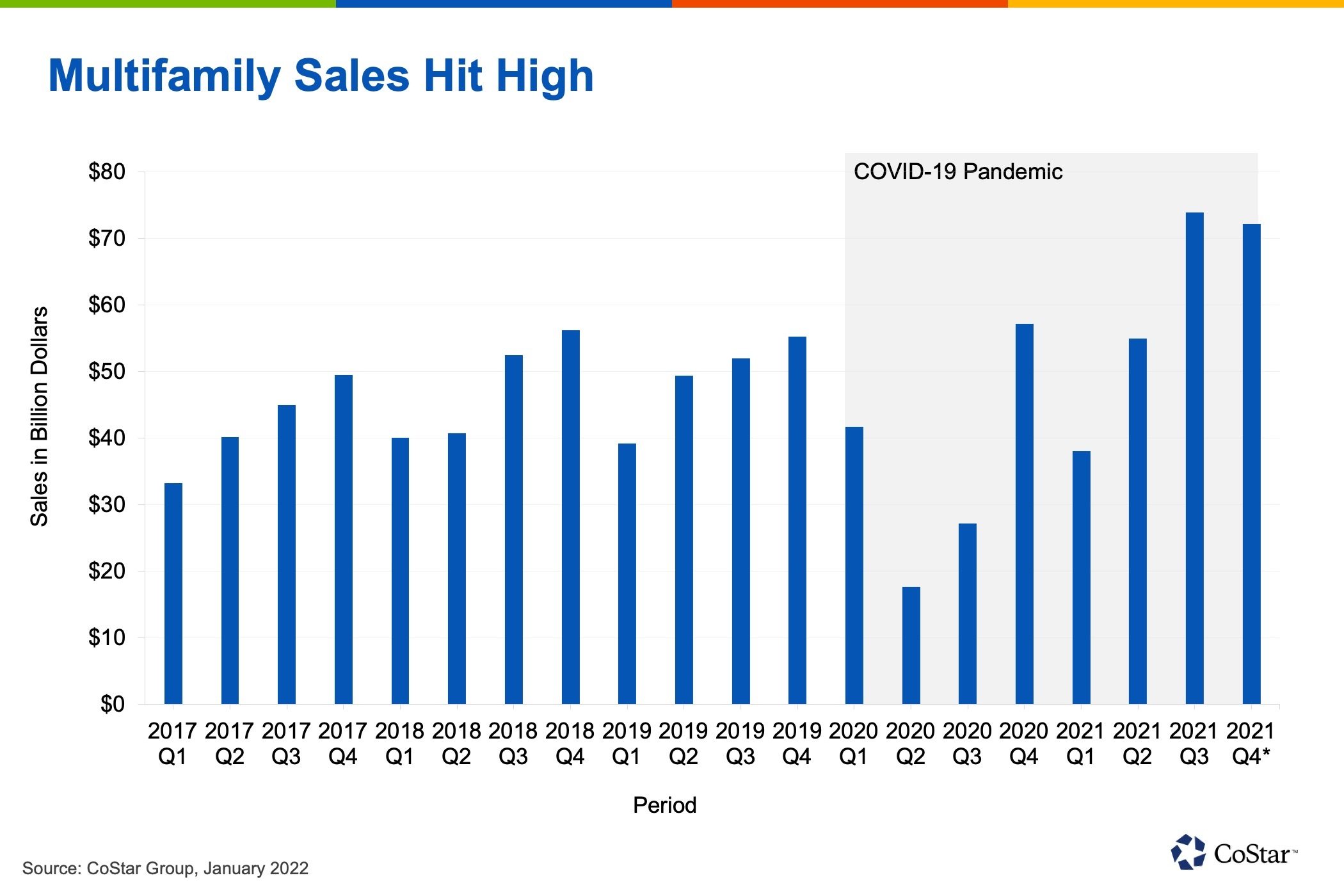
Further, those left behind in rental units are becoming more motivated to consider homeownership as apartment rents move ever higher. CoStar’s market rent series for U.S. apartments grew by 11.2 percent in 2021 — the highest rate of growth in the 21-year series. While the forecast calls for slower growth over the next five years, rents can be hiked annually or more frequently and are not as guaranteed as a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage, which helps make housing costs easier to budget and boosts potential demand for housing.
Yet inventories of homes for sale remain historically low. The National Association of Realtors reported 2.1 months of inventory in November, a record low, and Redfin reports that 26 days was the median number of days on the market for existing homes sold in the four-week period ending on Dec. 26, 2021, compared to roughly 50 days in the same period in 2019. During the pandemic, families were reluctant to move, depressing inventories. With a growing number of cases due to the omicron variant, the inventory of homes for sale should remain constrained through the early months of 2022.
At the same time, builders of new homes have faced rising costs of construction materials and labor, leading them to raise prices higher or choose to build homes with higher price tags. In the current environment of strong demand, it’s more likely the latter will occur. Private residential construction spending grew by 16.3% year over year in November.
It’s not all bad news. Rising prices have been a boon to homeowners who face financial difficulties by allowing them to refinance or sell at a profit, as home equity has been boosted. Some buyers expected a wave of distressed properties to reach the market in 2021 due to pandemic-related forbearance programs, but that never materialized. Mortgage data provider Black Knight reports that just 891,000 mortgages remained in forbearance as of Dec. 21, 2021, compared to a peak of roughly 4.7 million in May 2020.
At Some Point, Prices Should Decelerate
In reality, price increases at recent rates cannot sustainably continue unabated. At some point, erosion of affordability will limit the buyer pool, and that may be starting to happen. Fewer households can afford to buy a home at today’s prices than earlier in the pandemic, when incomes were supported through various government programs, such as stimulus checks and enhanced unemployment benefits. The National Association of Realtors housing affordability index fell to 148.2 in October 2021, roughly to 2017-2019 levels when the housing market was more balanced.
Furthermore, housing affordability has become a larger strain in high-cost-of-living areas such as San Francisco and Los Angeles. The housing affordability index in the U.S. West registers 111.9, compared to 200.9 in the Midwest.
To be sure, affordability has been buoyed by mortgage rates, which have been historically low despite a gradual increase to 3.1% in December from 2.7% a year ago for the average mortgage rate on a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage, according to Freddie Mac.
However, rates are expected to rise in 2022. The Federal Reserve announced last year that it would accelerate its winding down of asset purchases, including mortgage-backed securities. In its Summary of Economic Projections, the median projection calls for three rate hikes over the year, with three more likely coming next year. This would lead to higher long-term rates, which mortgages are usually tied to, and increase housing costs for buyers that wait to secure home loans.