In this article we are going to conduct an investment analysis on a 140 unit apartment building acquisition. We’ll walk through the process of forecasting cash flows and also explain the calculations needed to determine investment value. Read on as we take a deep dive into the world of apartment investing.
Apartment Investment Case Study Objectives
First, before we jump into the details of this investment analysis, let’s quickly go over our objectives. Here’s what we’ll accomplish in this case study:
- Forecast the before tax cash flows over a 5 year holding period for a 140 unit apartment building.
- Calculate the maximum supportable loan amount based on the debt service coverage ratio and the loan to value ratio.
- Calculate the gross rent multiplier.
- Calculate the cash on cash return.
- Calculate the debt service coverage ratio.
- Complete a discounted cash flow analysis to determine the levered and unlevered internal rate of return (IRR) and net present value (NPV).
- Stress test the vacancy rate to analyze how it impacts cash flow.
- Stress test the vacancy rate to analyze how it impacts the debt service coverage ratio.
- Stress test the loan interest rate to analyze how it impacts the debt service coverage ratio.
Apartment Investment Case Study Scenario
An investor is considering buying an apartment building with 140 units offered for sale at $16,500,000. The subject apartment building has the following unit mix:
Additionally, the following assumptions are also being made by the investor in order to construct a 5-year cash flow proforma:
Vacancy and Credit Loss
In the current market, vacancy and credit losses are running at 9%. Due to the improving market conditions as well as the investor’s prior experience leasing and operating multifamily buildings, it’s expected that vacancy will steadily decline over the next 5 years to 5%.
Potential Rental Income
Potential rental income is based on the above unit mix. The 1-bedroom and studio rental rates are expected to increase at 2% annually. The 2-bedroom units are also expected to increase at 2% annually.
Financing
After a preliminary discussion with a relationship manager at a local bank it’s determined that a loan can be extended based on the lesser of a 1.25x debt service coverage ratio or 80% loan to value. Additionally, assuming the underwriting process doesn’t reveal any red flags, it’s expected that the loan will be based on a 20 year amortization and a 6% interest rate.
Operating Expenses
The following table breaks out historical operating expenses for the property as well as projected increases over the holding period.
Reserves for Replacement
In addition to the above operating expenses a reserve for replacement of $250 per unit will also be included in this analysis.
Sales Price and Cost of Sale
The projected sale price is estimated by applying a conservative 3% annual growth rate to the acquisition price of the property over the 5 year holding period. Additionally, a 6% cost of sale is factored into the net sales proceeds to account for selling costs.
Acquisition Costs
In addition to the $16,500,000 purchase price, an additional $50,000 is factored in to account for closing costs.
Discount Rate
For the purposes of this case study we’ll assume that the investor’s discount rate, or required rate of return, is 15%.
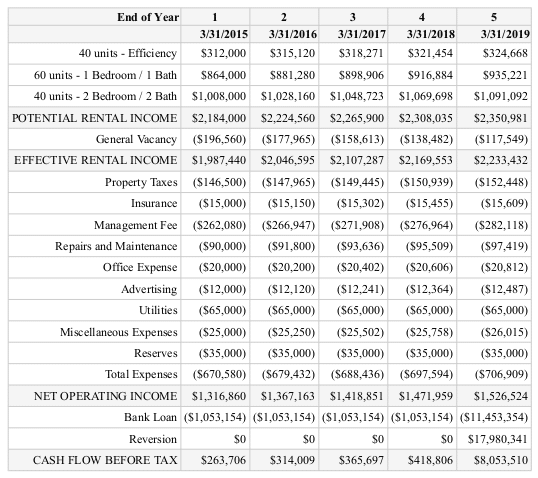
Apartment Investment Proforma
Using the above assumption we can now build a proforma for the proposed apartment investment property. This can be accomplished in Excel in a few hours, or in our case we did this entire analysis in less than 10 minutes.
Now that we have a 5 year proforma, let’s take a look at what the maximum supportable loan amount is based on these cash flows. Using the above 1.25x DSCR and 80% LTV assumptions we get the following:
As shown above, the maximum loan analysis based on year 1 proforma NOI is about $12,250,000. Assuming we can get this loan amount approved at the 6% rate amortized over 20 years, this is the updated proforma:
You’ll notice that the debt we added to the property reduced our cash flow significantly, however, this also reduces our equity requirement and therefore improves yield. We’ll discuss this in more detail below, but first let’s take a look at some quick ratios:
Year 1 cash on cash return is 6.14%. At first glance this is well below our target rate of return of 15%, However, because the cash on cash return only takes into account a single year instead of the entire holding period, the IRR and NPV below will be much more relevant for our purposes.
The gross rent multiplier is 7.58x, which taken by itself doesn’t mean much. However, assuming we have some other submarket data to compare this to we can check whether or not it’s in line with comparable properties. The important take away here is to check whether or not the gross rent multiplier is abnormal, and if so, to further investigate why.
The debt service coverage ratio is in line with the bank’s requirement of 1.25x and improves over the holding period. This is partially due to our assumption of increasing occupancy over our investment horizon, as well as increasing rental rates. We’ll stress test these assumptions further below, but at first glance the DSCR is adequate for this deal.
Finally, the breakeven occupancy on this property is just under 79%. This means total vacancy can go up to 21% and the property will still produce enough cash flow to cover expenses and debt service. Good to know.
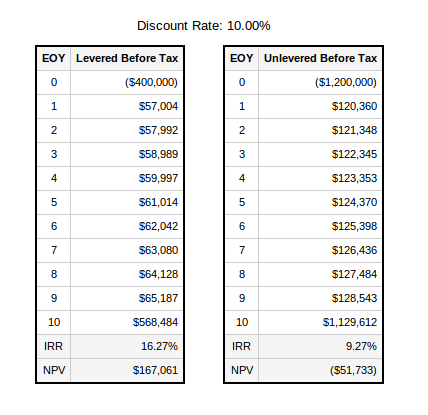
Apartment Discounted Cash Flow Analysis
Screening this property with the above ratios is a good starting point, but ultimately a full discounted cash flow analysis should be completed to determine IRR and NPV:
As you can see above, the levered internal rate of return comes in at 18.65%. While the above Year 1 cash on cash return didn’t meet our required rate of return of 15%, the full discounted cash flow analysis shows that the yield on this investment comfortably exceeds our target return. In fact, the net present value tells us that we can pay about $650,000 over the asking price and we’ll still achieve our target yield. This can come in handy during negotiations, especially in a competitive bidding situation.
Apartment Investment Sensitivity
So after a quick first pass it appears that this potential acquisition meets our target yield based on some reasonable assumptions. However, what if our assumption of a declining vacancy rate, from 9% in Year 1 to 5% in Year 5, turns out to be overly optimistic? Let’s take a look at what we deem to be a worst case scenario – that the market vacancy rate actually deteriorates after we acquire the property to 15%, rather than the current 9%. How will this impact our IRR?
While a worse than expected vacancy rate does reduce our cash flow, it turns out that we’d still achieve our target yield of 15%. What about the debt service coverage ratio? Will a higher than expected vacancy rate violate our 1.25x DSCR loan covenant? Let’s take a look at what happens to the debt service coverage ratio as we move from a 6% vacancy rate all the way up to a 20% vacancy rate:
As shown above, in Year 1 we actually can’t support a 1.25x DSCR requirement at a vacancy rate of 10%. While this does improve over the holding period, this could be problematic for us if the market turns out worse than expected. This could also be discovered during the loan underwriting process, resulting in a lower loan amount or stronger loan covenants. This information might come in handy during negotiations.
Next, let’s take a look at how sensitive our DSCR is to our loan interest rate. This is useful in understanding how much wiggle room there is in negotiating the interest rate with our bank, as well as understanding how capital market conditions might affect the buyer of our property at the end of the holding period.
As shown above, 6% appears to be the upper limit loan interest rate based on Year 1 cash flow. Once the rate gets beyond 6% it starts eating into our 1.25x DSCR requirement. However, in subsequent years, assuming we hit our projections, the property can support a much higher interest rate based on the same loan amount. This provides some cushion toward the end of our holding period, in case the then prevailing market conditions change and interest rates rise.
Conclusion
While there are several different angles you can look at when underwriting a potential acquisition, this simple case study illustrates a few core concepts. First, sizing up a loan amount based on proforma cash flow. Second, calculating and interpreting several quick but useful ratios. Third, understand whether or not an acquisition meets a target yield. And finally, understanding how changes in our assumptions affect our resulting cash flow and underwriting ratios. While there are several additional layers of analysis we can dive into for a property like this, the above analysis gives us a good starting point for screening this particular property.
Source: Apartment Investing Case Study
https://www.creconsult.net/market-trends/apartment-investing-case-study/