For commercial real estate investors, having access to as many metrics as possible to provide insight and comparison opportunities is critical. Various metrics are available, including cash-on-cash return and internal rate of return, enabling investors to compare properties more closely when deciding which to choose for investment.
Most investors set their own threshold of what is acceptable to meet their needs or to ensure they hit a certain target before investment. Yet, when investors consider dozens of opportunities each day, it is helpful to have a straightforward metric to help compare properties. These two figures are core components, and knowing the difference between IRR and cash on cash is critical.
What Is Cash on Cash Return (CoC Return)?
The cash-on-cash multiple is a type of rate of return ratio. It provides insight into the total cash earned for a property over the total cash invested into the property. It is based on cash flow before tax within a specific period divided by the equity that’s invested at the end of that period.
Cash on cash return (CoC) is a levered metric or an after-debt metric. By comparison, an unlevered metric is “free and clear” returns. Investors use this metric as a way to assess an investment opportunity.
Cash on Cash Return Formula
The formula for cash on cash return is rather simple:
Annual Net Cash Flow divided by Invested Equity equals Cash on Cash Return
In most cases, this is expressed as a percentage. When it comes to the cash-on-cash calculation, real estate investors typically look at their investment return.
How to Calculate Cash on Cash Return
Applying the formula above, here is an example of how the cash-on-cash works (you can also use a cash-on-cash calculator to help you with this process.)
Bob wants to purchase a multitenant property for $1 million. He puts in $250,000 in equity in the deal. He then finances the $750,000. In this example, the equity investment is $250,000. (Now, this does not include things like closing costs which would also be factored into the equity if paid out of pocket).
After a year, the property provides an annual rental revenue of $120,000. Mortgage payments on the property total $55,000. In addition, Bob invests another $20,000 into the property improvements.
To determine the cash on cash return, the first step is to determine the annual net cash flow for the property. In this situation, the annual cash flow for the property follows this formula:
- Total Gross Revenue minus Total Expenses
In our example, the annual cash flow is $120,000 minus $75,000 or $45,000.
Next, to get the Cash on Cash Return, we need to divide the annual net cash flow by the amount of equity put into the property, in this case, $250,000.
The equation is $45,000 divided by $250,000 equals 18%.
This figure means that the total cash on cash return for that property is 18%. That also means that the investment’s profit for the year will be 18% of the amount of cash that is invested initially.
What Is a Good Cash-on-Cash Return?
Investors typically need to seek out their own answer to this since it is very much dependent on what their needs are and preferences goals are. For some investors, earning 8 to 10% cash on cash return is enough for them. Others do not consider options under 20% cash on cash yield.
Limitations of Cash on Cash Return
There is no doubt that cash on cash return is an important factor to consider, but it has some limitations. For example, it is a simple calculation that measures investment performance. Use it as a starting point when considering investment properties, and then dig deeper into other metrics for more insight. CoC often does not consider things like the length of investment of operating cash flows within a holding period or the reversion cash flow that comes from the sale of the property later.
What Is IRR (Internal Rate of Return)?
Another key figure is the IRR formula. Understanding IRR in real estate can provide more opportunities for you to see the difference in these funding methods. Cash on cash does not account for what investors call the time value of money, but this is where IRR comes into play.
Internal rate of return (IRR) is the interest rate that makes the net present value of all of the property’s cash flow zero. Another way to look at it is the actual annual growth rate calculated by isolating compounding interest’s effects in situations where the investment is more than a year.
Internal Rate of Return Formula
The formula for this metric is complicated and typically not done by hand. Rather, it’s best to utilize Excel or another program for calculating it.
The formula for Calculating IRR
Here is what the formula looks like:
In this,
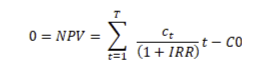
Ct=Net cash inflow during the period
C0=Total initial investment costs
IRR=The internal rate of return
t=The number of time periods
You can learn more about setting up Excel to calculate this by visiting this link.
What Is a Good Internal Rate of Return?
What is a good IRR? Again, that’s subjective and really depends on the investor’s goals and needs. Most of the time, a 5-year IRR should be around 15% or higher, and sometimes it can be much higher than this.
Limitations of IRR
IRR aims to provide insight into the total return on investment by incorporating compounding interest into the process. However, when IRR is high, that does not always mean that the investment is seeing a cash flow at the current time. That is because this metric also uses the final sale or the existing assets as a component of the formula. That makes it impossible to be the only factor considered during this process.
What’s the Difference Between IRR and Cash on Cash Return?
IRR is the total interest earned on the money the investor puts into the project. The difference between this and CoC is that IRR is focused on the total income earned throughout the investor's complete ownership of the property, whereas CoC provides an annual segment view of the property.
Cash on Cash Return vs. IRR: Which One Should You Use?
IRR is much harder to calculate and typically requires having a significant amount of data about the property at the time of estimating. However, it is worth using both metrics. Often CoC is the first step to weed out less-than-desirable properties. Then, before investment, investors take a closer look at these metrics to provide a more comprehensive review of the investment’s opportunities.
Wrapping Up
What is a good cash-on-cash return? When should you use IRR? These are very important questions.
The key here is that commercial real estate investors should have as many metrics as possible available to them to use to determine which property could be ideal and which meets their very specific needs or goals. It’s not often a question about which one to use but how a property looks using both of these metrics.
Source: Cash on Cash Return vs IRR: Understanding the Difference
https://www.creconsult.net/market-trends/cash-on-cash-return-vs-irr-understanding-the-difference/





